What Is the Marketing Process
The marketing process is the heartbeat of any business strategy—a structured journey from understanding market needs to delivering value and generating revenue. Imagine it as a GPS guiding your brand from the foggy unknown to a clear destination: customer loyalty and business growth. It’s not just about flashy ads or witty slogans; it's a full-circle system involving research, planning, strategy, execution, and optimization. At its core, the marketing process helps businesses identify what customers truly want, build a plan around those needs, execute campaigns effectively, and continually refine tactics based on feedback and performance. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution but a customizable framework that evolves with market trends, consumer behaviors, and business goals.

Why It Matters for Business Growth
Why is the marketing process important? It's important because, without it, businesses may lose direction. A strong marketing process helps companies make smart choices based on real information and careful planning. It guides decisions on which product to launch and the best ways to promote it. Additionally, it ensures that different departments work together efficiently, which saves time and money. Furthermore, it helps build strong relationships with customers, making them feel valued and understood, ultimately supporting long-term business success.
In today’s competitive landscape, skipping the marketing process is like trying to bake a cake without a recipe—you might get lucky, but chances are it won’t rise. With tools like Denote, marketers can streamline research, analyze competitor data, and centralize campaign assets, making the process smoother and more effective.
Stage 1 - Market Research
Identifying Customer Needs
All successful marketing starts with empathy—understanding your customers at a deep level. What are their pain points? Desires? Habits? This is where the marketing process truly begins. Conduct surveys, run interviews, monitor social conversations, and dive into review platforms. Don’t assume you know what people want—prove it with real insights.
Use both types of methods: qualitative and quantitative. The numbers reveal what is going on, while talking to people helps you understand the reasons behind it. By combining these methods, you create a strong foundation for making well-informed decisions.
Analyzing Competitors and Industry Trends
You’re not working alone. By examining what your competitors are doing, you can understand what is successful in your industry and find opportunities where you can stand out. Tools like Denote are useful because they let you see and analyze ad designs, messaging, and how audiences respond to various brands. It’s important not to just focus on companies that are exactly like yours. Sometimes, the biggest challenge or best new idea can come from a completely different industry that is targeting a similar audience. Keep your eyes on industry reports, watch which hashtags are trending, and stay informed about the latest technologies that are coming onto the scene.
Using Tools for Effective Research
The digital age has blessed marketers with an arsenal of tools. Use Google Trends to monitor topic popularity, leverage surveys via Typeform or SurveyMonkey, and analyze online behavior through platforms like Hotjar or Crazy Egg.
Denote stands out by helping you organize your research in one visual space—ads, screenshots, articles, and creative assets can be stored, tagged, and reviewed easily, improving collaboration across your team.
Stage 2 - Setting Marketing Objectives
SMART Goal Framework
Once you have your data, it's time to take action based on what you've learned. SMART goals can help with this. They stand for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Using SMART goals makes sure your marketing plans are not only big but also something you can actually do.
For example, instead of just saying you want to "increase website traffic," you could set a more detailed goal like "increase website traffic by 25% within 3 months by using content marketing strategies." This is like giving a GPS clear directions instead of just saying "go north." SMART goals give you a clear path so you know exactly what you’re aiming for and how to get there. This approach helps you focus your efforts and resources on what truly matters, ensuring that your objectives are not just dreams but actual plans you can work toward.
Aligning Marketing Goals with Business Objectives
Marketing teams often tend to focus too narrowly on specific tasks, missing the bigger picture. To avoid this, it's important that your marketing goals support the company's main objectives. If the company's focus is on retaining current customers, then your marketing should aim to keep these customers engaged and loyal, rather than trying to bring in new leads. In environments where multiple teams must work together, using shared tools, such as project dashboards, can really help everyone stay informed and aligned. Additionally, Denote’s collaborative asset management features can enhance transparency and foster teamwork. These tools ensure that teams can see what everyone is doing and collaborate more effectively.
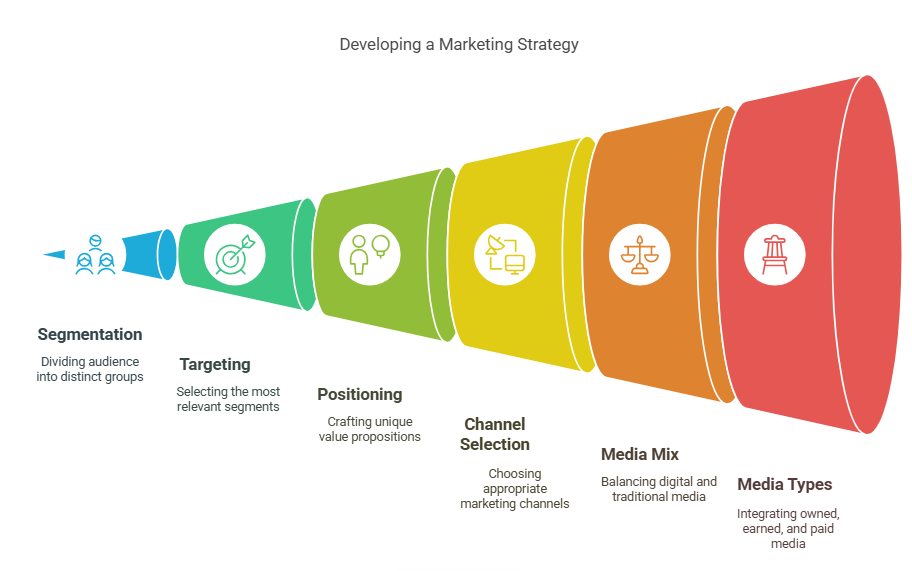
Stage 3 - Developing a Marketing Strategy
Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP)
Here’s where strategy starts to take shape. STP is the holy trinity of audience understanding:
Segmentation: Break your audience into smaller groups based on demographics, behavior, or needs. Targeting: Choose the segments you can serve best. Positioning: Craft a unique value proposition for each target.
You don’t speak the same way to a Gen Z buyer as you do to a corporate CFO. Tailoring your message is key.
Choosing the Right Channels
Different marketing channels work better for different people. To find the best ones for you, it's important to know where your audience spends their time online and what kind of content they enjoy and interact with. Instead of following popular trends, think carefully—while TikTok is currently very popular, LinkedIn might be more valuable for your business if your potential customers are there. Focus your efforts where they'll have the most impact.
Digital vs Traditional Media
Digital media is easy to change, grow, and measure. On the other hand, traditional media, like TV, print, and radio, gives you a chance to reach many people and helps make your brand more trustworthy. Often, using both digital and traditional media together gives the best results. This choice depends on what you want to achieve and how much money you have to spend. Digital media lets you try different things and adjust them easily, while traditional media helps you build your brand's trust with a large audience. So, a mix of both can be very effective for reaching your goals.
Owned, Earned, and Paid Media
- Owned Media: Your website, email list, blog—content you control.
- Earned Media: PR mentions, shares, and word-of-mouth—essentially free marketing.
- Paid Media: Social ads, PPC, influencer partnerships.
A well-rounded marketing process blends all three. Think of them as a balanced diet: owned is your home base, earned is your social proof, and paid is your growth steroid.
Stage 4 - Marketing Execution
Campaign Planning and Rollout
Execution is where strategy meets action. Begin with a clear campaign brief: objectives, messaging, timeline, KPIs. Set deadlines and assign roles. Don’t forget contingency planning—life (and markets) are unpredictable.
Use content calendars and project management tools to avoid chaos. The smoother the launch, the faster you’ll start seeing results.
Cross-Functional Team Involvement
Marketing is not a solo activity. It works closely with sales, product teams, and customer support. Each of these parts is crucial for success. To achieve good results, it's essential to get everyone involved from the start and maintain regular communication.
Consider setting up weekly meetings to keep everyone aligned. Use shared dashboards to provide real-time updates and insights, making it easier for different departments to stay informed. Also, use a centralized storage system, such as Denote, to keep all materials organized and accessible to everyone involved. This organization ensures that everyone can find what they need quickly and easily, promoting smooth collaboration across all teams.
Tools and Platforms for Execution
There’s no shortage of platforms to bring your marketing campaigns to life:
- Email: Mailchimp, ConvertKit
- Social Media: Buffer, Hootsuite
- Design: Canva, Figma
- Analytics: Google Analytics, Mixpanel
- Ad Management: Meta Ads Manager, Google Ads
Denote fits in as a complementary tool—ideal for organizing ad creatives, analyzing competitor campaigns, and streamlining your team's creative process.
Stage 5 - Monitoring and Optimization
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Launching a campaign is just the beginning. Once it's up and running, the real work starts. It's important to keep an eye on key numbers like CTR (Click-Through Rate), conversion rate, CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost), and ROI (Return on Investment). These measurements help determine if your plan is on track or needs some adjustments.
These numbers are meaningful. For example, if many people open your emails but few take further action, it might mean your offer isn't appealing enough. In this situation, you should examine the details more closely to figure out what's going on. Looking deeper at the data can help improve the campaign's success.
Feedback Loops and A/B Testing
Trying to optimize without feedback is like steering a ship with your eyes closed. It's important to gather data from all sources—users, analytics tools, and team observations. Use this data to test your ideas through A/B testing. Small changes, such as altering the headline's wording, adjusting the button color, or changing the email send time, can have a significant impact on performance. Think of the data as your guide or compass in making decisions.
Continuous Improvement
Successful marketing teams are always learning. They regularly check their performance every month, reflect on past actions, and make necessary improvements. They also keep a record of their successes and failures.
To enhance their strategies, they use a structured approach. They combine internal evaluations with customer feedback and compare their performance to industry standards. This constant cycle of review and improvement helps them strengthen their marketing process and ensures each new campaign is better than the last.
Real-World Examples of Successful Marketing Processes
Case Study 1: SaaS Product Launch
A mid-sized SaaS company wanted to launch a new feature. Using the marketing process, they:
- Researched customer pain points and identified demand.
- Set SMART goals around signups and engagement.
- Crafted a multi-channel strategy across email, webinars, and paid search.
- Used Denote to analyze competitor landing pages and ad creatives.
- Executed the campaign with a cross-functional team.
- Monitored results and adjusted messaging based on click and bounce rates.
The result? A 45% increase in feature adoption within 60 days.
Case Study 2: eCommerce Campaign
An online fashion retailer leveraged the marketing process to clear out seasonal inventory:
- Identified overstock items and customer purchase patterns.
- Created urgency-driven promotions targeting segmented audiences.
- Used influencer marketing and email blasts.
- A/B tested ad formats and subject lines.
- Tracked KPIs in real time.
By the end of the quarter, they had not only sold the stock but also increased email subscriber engagement by 30%.
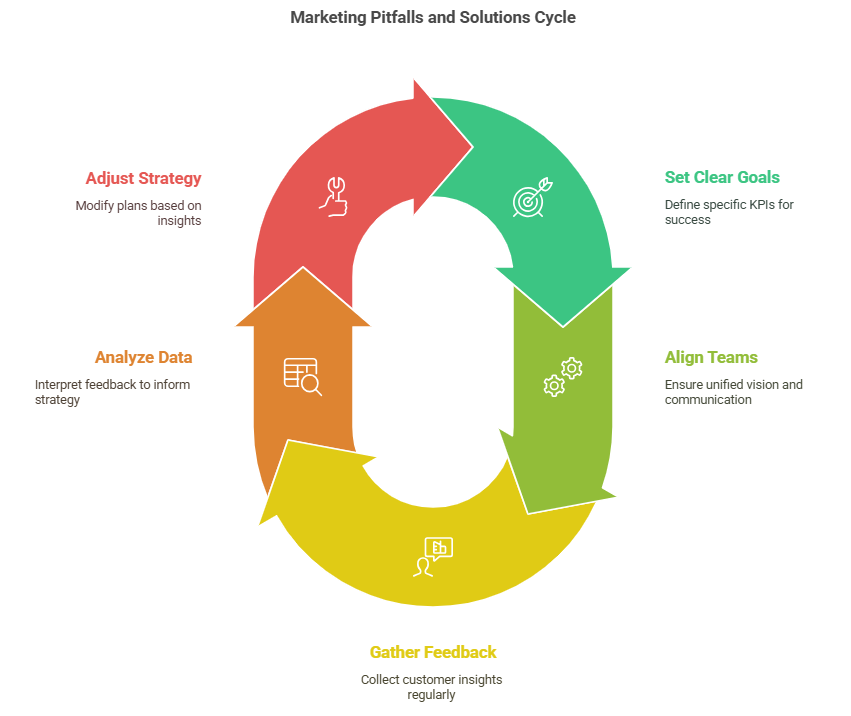
Common Pitfalls in the Marketing Process
Lack of Clear Goals
Many campaigns don't succeed because their goals aren’t clear. Without specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), you can't measure if the campaign is doing well or if you need to make changes. Being specific about goals helps in knowing what success looks like and when you might need to try a different approach. Always aim for clarity to ensure you're on the right path.
Misalignment Between Teams
When the product team has one idea and the marketing team has a different idea, it leads to confusion. To prevent this, it's important to start with everyone on the same page. Use tools that allow everyone to see and contribute to the plan, and maintain clear and open communication among all team members.
Ignoring Customer Feedback
This is a hidden risk for many plans. Your customers and audience always have opinions and feedback to share—are you truly listening to them? Make use of surveys to get direct responses, read reviews to understand their thoughts, follow social media where they often express their views, and talk with your sales team who interact with them regularly. This way, you can stay better connected and aware of what people really think and need.
Conclusion
The marketing process isn’t a buzzword—it’s a powerful framework that fuels clarity, creativity, and results. Whether you’re a scrappy startup or a growing enterprise, mastering each stage—from research to optimization—will sharpen your marketing edge.
.jpg)
